Smart Remote Extended Reality Teleconsultation and Product Guidance
Smart remote extended reality (XR) teleconsultation and product guidance has two important lines of work, 1) detection of machinery parts or objects in the scene, identifying the used tools or machinery and specifically tailored guidance for this machinery, and 2) reconstruction of the local scene to enable remote experts dialing in via teleconsultation to provide additional guidance. Teleconsultation and XR guidance can overcome the lack of workforce to guide and instruct maintenance or provide in-situ support.
Smart Extended Reality Product Guidance
During her first year of her PhD, Hannah focused on XR guidance and detecting machinery or objects in scenes. Together with Constantin, they collaborated on a project from the Medical Augmented Reality Summer School (MARSS), developing an approach called ARTFM, which addressed surgical instrument assembly and detection using a CNN trained on synthetic data. Their work was rewarded at MARSS 2021 with the first place. The initial project employed approximated 3D positions. A further project combined 3D mesh information and object detection for guiding blind and visually impaired people [6, 7]. Her subsequent work involved improving 6D pose estimation and integrating assembly states into the process [2, 4]. GBOT [4] and ASDF [2] utilized relative object poses and assembly state detection to enhance 6D object tracking and pose estimation. They relied solely on synthetic training data. In a collaboration with the CAMP chair, Hannah addressed challenges posed by texture-less or reflective surfaces of objects, contributing the Housecat6D dataset, which was highlighted at CVPR 2024.
Smart Remote Extended Reality Teleconsultation and Product Guidance
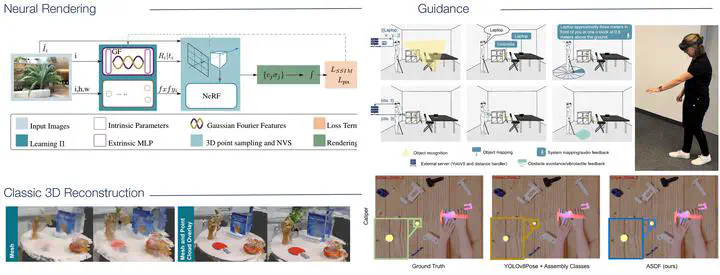
Currently, Hannah is working on integrating smart 3D reconstruction into the guidance workflow. Therefore she focuses on the second aspect of XR teleconsultation and product guidance involving reconstructing the local environment to the remote user. Standard mesh-based or point cloud-based 3D reconstructions are often non deep learning driven and enable fast data processing [12]. Combining classic 3D reconstruction methods we guide the user to the currently captured part of the scene [12]. However, approaches like neural rendering further allow novel views and provide a more high-fidelity reconstruction which can be beneficial for in-body 3D reconstruction. One essential aspect of neural rendering methods are the accurate camera poses [10, 11]. XR setups, consisting of multiple varying cameras (XR glasses, RGB-D cameras etc.). These cameras further have different intrinsic camera parameters, our approach NeRFtrinsic Four [11] enables the optimization of multiple intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters, thereby enhancing neural rendering.
[1] Kleinbeck, C., Schieber, H., Andress, S., Krautz, C., & Roth, D. (2022, March). ARTFM: Augmented Reality Visualization of Tool Functionality Manuals in Operating Rooms. In 2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW) (pp. 736-737). IEEE.
[2] Schieber, H., Li, S., Corell, N., Beckerle, P., Kreimeier, J., & Roth, D. (2024). ASDF: Assembly State Detection Utilizing Late Fusion by Integrating 6D Pose Estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.16400.
[3] Jung, H.,* Zhai, G.,* Wu, S. C.,* Ruhkamp, P.,* Schieber, H.,* Rizzoli, G., … & Busam, B. (2024). HouseCat6D–A Large-Scale Multi-Modal Category Level 6D Object Perception Dataset with Household Objects in Realistic Scenarios. CVPR 2024, Highlight, *shared first author
[4] Li, S., Schieber, H., Corell, N., Egger, B., Kreimeier, J., & Roth, D. (2024). GBOT: Graph-Based 3D Object Tracking for Augmented Reality-Assisted Assembly Guidance. IEEE VR 2024
[5] Schieber, H., Demir, K. C., Kleinbeck, C., Yang, S. H., & Roth, D. (2024). Indoor synthetic data generation: A systematic review. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 103907.
[6] Schieber, H., Kleinbeck, C., Theelke, L., Kraft, M., Kreimeier, J., & Roth, D. (2024, January). MR-Sense: A Mixed Reality Environment Search Assistant for Blind and Visually Impaired People. In 2024 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and eXtended and Virtual Reality (AIxVR) (pp. 166-175). IEEE.
[7] Schieber, H., Kleinbeck, C., Pradel, C., Theelke, L., & Roth, D. (2022, March). A mixed reality guidance system for blind and visually impaired people. In 2022 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW) (pp. 726-727). IEEE.
[9] Demir, K. C., Schieber, H., Weise, T., Roth, D., May, M., Maier, A., & Yang, S. H. (2023). Deep learning in surgical workflow analysis: A review of phase and step recognition. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.
[10] Schischka, N.,* Schieber, H.,* Asim Karaoglu, M.,* Görgülü, M.,* Grötzner, F., Ladikos, A., … & Busam, B. (2023). DynaMoN: Motion-Aware Fast and Robust Camera Localization for Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields. arXiv e-prints, arXiv-2309., *shared first author
[11] Schieber, H., Deuser, F., Egger, B., Oswald, N., & Roth, D. (2023). Nerftrinsic four: An end-to-end trainable nerf jointly optimizing diverse intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09412.
[12] Schieber, H., Schmid, F., Zollmann, S., & Roth, D. (2023, October). A Modular Approach for 3D Reconstruction with Point Cloud Overlay. In 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) (pp. 609-610). IEEE.
Hannah is supported by a scholarship from Siemens Healthineers and the Digital Health Innovation Platform (d.hip). Thank you!
